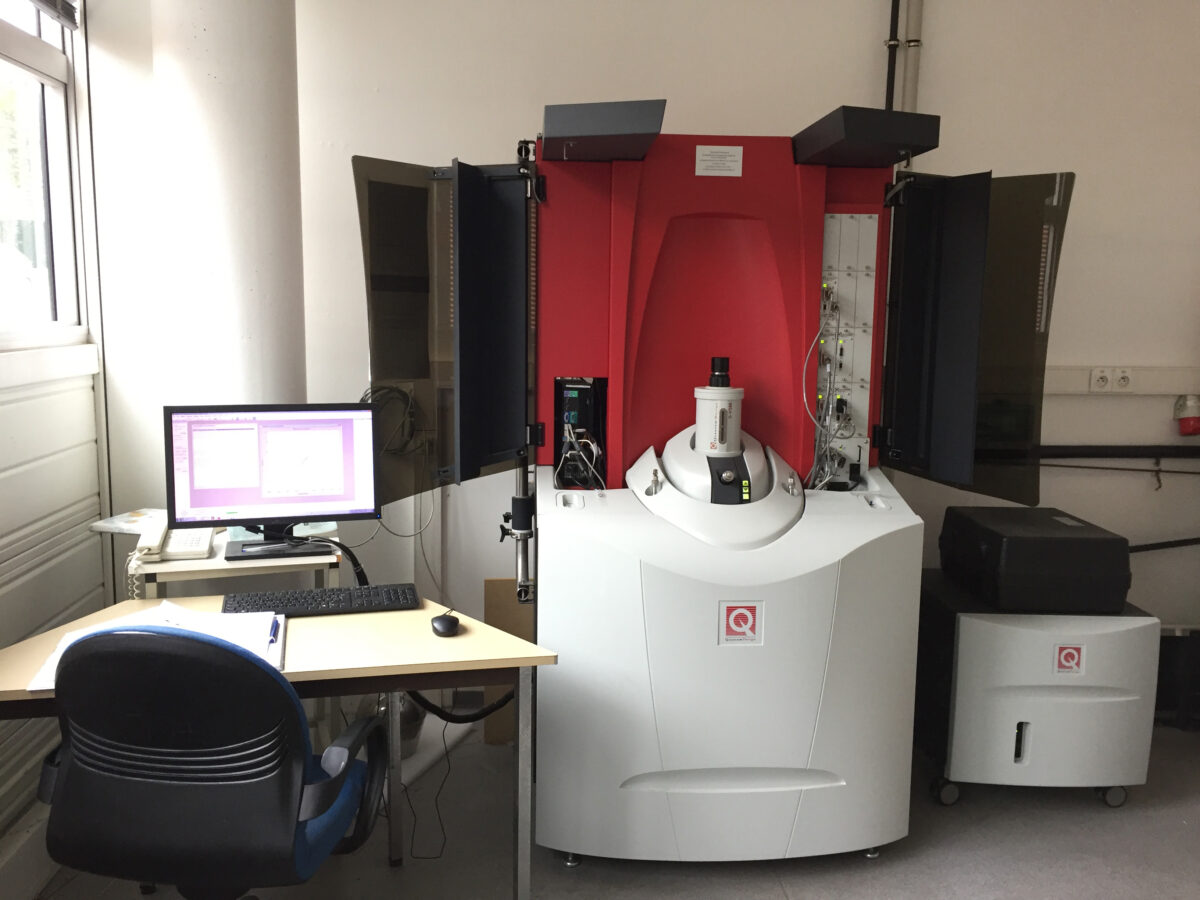
Principle of measurements: A measurement consists in moving a sample through superconducting detection coils (gradiometers), at a given temperature and in homogenous magnetic field. The gradiometer coils are accurately balanced. As a sample is moved through the coils, the magnetic moment of the sample induces an electric current in the detection coils. Since the coils, the connecting wires and the SQUID input coil form a closed superconducting loop, this current is not damped and any change in magnetic flux in the detection coils produces a proportional change in the persistent current in the detection circuit. Thus, by moving the sample from one side of the gradiometer to the other, a flux integration is performed. A flux transformer enables to transmit the gradiometer signal to the SQUID. The SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) is the most sensitive device available for measuring magnetic fields and is an extremely sensitive current-to-voltage convertor. The magnitude of the measured signal is proportional to the magnetic moment of the sample.
Quantum Design Magnetic Property Measurement System (MPMS-VSM):
Types of measurements :
— magnetization, hysteresis cycles
— susceptibility measurements
— alternative (AC) susceptibility measurements
Magnetic field (superconducting magnet) : +/- 7 Tesla
Temperature range : 1.8 to 400K
Measuring range :
— DC/RSO mode : +/- 2 emu
— AC mode : frequency : 0.1-1000 Hz, amplitude of the oscillating field : 0.1 to 10 G
Sensitivity : 10-8 emu at 1 T; 10-7 emu at 2 T; 5.10-7emu at 7 T
Types of samples :
— platelets (dim. max. : 4 x 4 mm2)
— powder samples (few mg, typically 10 mg), crystals, gels
— thin films
Measurement duration :
— cycles +/- 7 T : 2 to 5 hours
— susceptibilities (DC or/and AC or/and VSM) : 7 hours (300 K – 1.8 K)
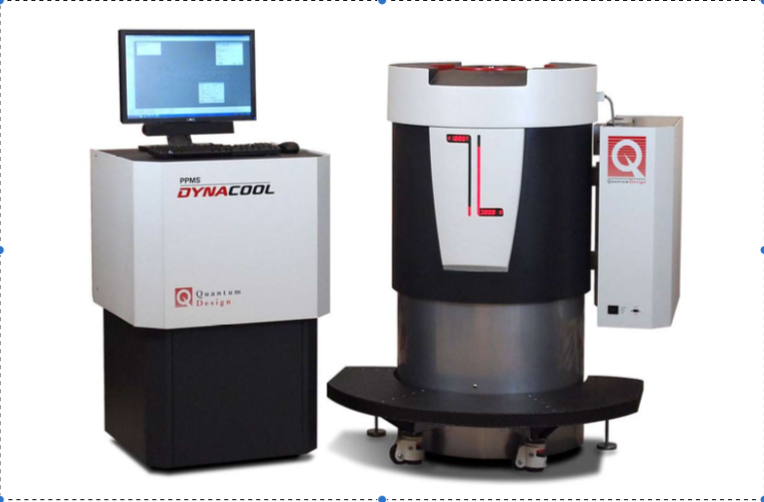

The Physical Properties Measurement System (PPMS) measures the transport properties and specific heat of materials as a function of temperature and/or magnetic field.
A supply of liquid helium ensures cooling of the superconducting magnet and allows temperature variation of the samples. Liquid helium is produced in a closed circuit, and the instrument consumes one bottle of compressed helium per year.
The magnetic field can be swept between +9T and -9T in 10 min. at a maximum rate of 20 mT/s.
Temperature can be scanned from 400K to 1.8K in 40 min minimum.
Samples are thin films of approx. 5×5 mm². Powder can also be measured for specific heat. 3 samples can be measured simultaneously for transport properties.
Specifications:
- 2 or 4-wire electrical transport measurements.
Applied current: 10 nA-8 mA, 5 Hz square-wave signal
Measured voltage: 1 mV-4V Resistivity range: fraction of an ohm-10 MΩ.
- Specific heat measurements :
Typical range 1-103 µJ/K
Sample holder:(diameter=2.5 cm)
Contact :


