The IPCMS thin films technical platform is composed with the following deposition technics: pulsed laser deposition, molecular beam epitaxy, evaporation and sputtering. The obtained ceramic, metallic and/or organic thin films/heterostructures are used for several applications such as photovoltaic, spintronic, superconductivity spin-wave propagation, energy harvesting and capacitors technologies.
PULSED LASER DEPOSITION (PLD)
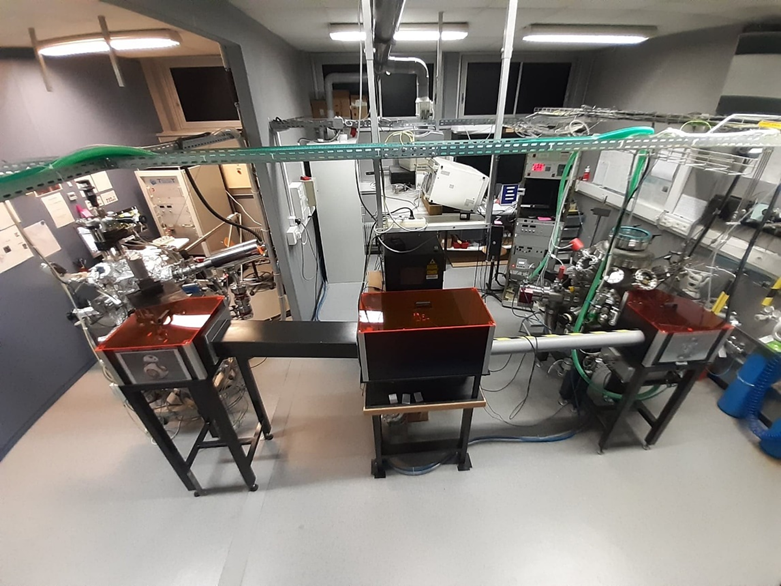

The Inorganic Materials Chemistry Department (DCMI) at the IPCMS has two pulsed laser deposition chambers which are used to elaborate functional oxides thin films such as:
- Magnetoelectric compounds: Ga2-xFexO3
- Double perovskite Bi2FeCrO6 for photovoltaic applications
- Rare earth nickelate: NdNiO3
- Spinel: FeV2O4, VFe2O4, GeFe2O4, CoFe2O4
- Lanthanum strontium manganite: La1-xSrxMnO3
A detailed description of the equipment is available here
More informations about the reasearch projects are available here
Contacts :
Scientific in charge
HYBRID GROWTH CLUSTER
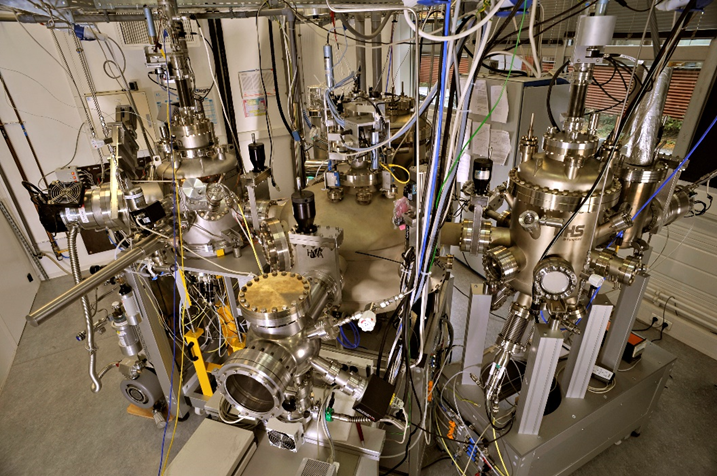
The need for hybrid heterostructures made of thin films of both organic and inorganic materials have driven the development of a dedicated facility at the Department of Magnetic Object on the NanoScale (DMONS).
The hybrid cluster gathers around a robotized transfer chamber, 3 different growth chambers, each one dedicated to the growth of different materials: a sputtering chamber for the growth of metallic thin films (Co, Fe, Cr…) or simple oxides (MgO); a chamber dedicated to the evaporation of metallic thin films (Au, Co…); and a chamber dedicated to the molecular beam epitaxy of organic materials (OMBE) for the growth of organic thin films (C60, phtalocyanines, oxocarbic acids…).
The facility allows for the fabrication of organic-inorganic heterostructures in an ultra-high vacuum environment (10-10 mbar in all the chambers) during the whole fabrication process. Each growth chamber is equipped with an oven for the samples and quartz microbalances.
More informations about the equipment are available here
Projects :
Research performed on the hybrid cluster facility is focusing on heterostructures based on organic thin films materials for energy harvesting based on spintronic devices (Co-CoPc), on heterostructures based on spin-crossover molecules (Fepyrz) or even on (anti)ferroelectric molecules for high energy density capacitors (croconic acid).
Contacts :
Engineer
Scientific in charge
MOLECULAR BEAM EPITAXY (MBE)
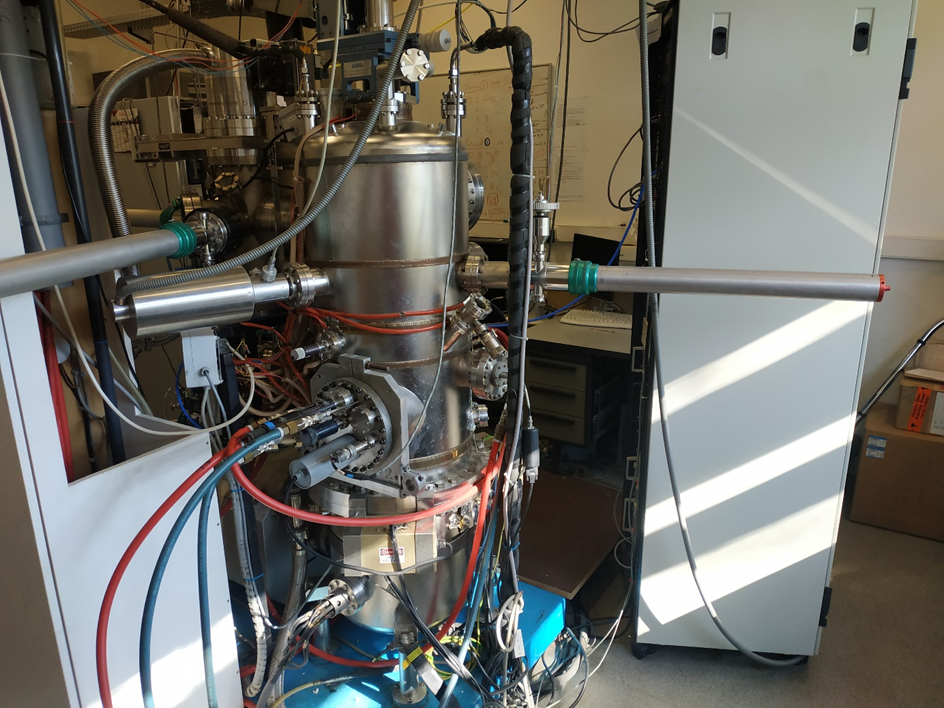
The department of Magnetic Object on the NanoScale (DMONS) at IPCMS is managing a Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) chamber dedicated to the growth of metals thin films.
The chamber is equipped with two electron guns with 4 crucibles each allowing to deposit up to 8 different materials in an ultra-high vacuum (10-10 mbar) environment. The growth is controlled by two quartz microbalances and followed by electronic diffraction RHEED (reflective high energy electron diffraction).
More informations about the equipment are available here
Projects :
Today, this epitaxial system allows to fabricate metallic heterostructures for the studies of spin-wave propagation (FeV), corrosion resistive alloy (Fe/Cr), or even the growth of europium oxide on graphene.
Contacts :
Engineer
Scientific in charge

EVAPORATION (ELECTRON BEAM)
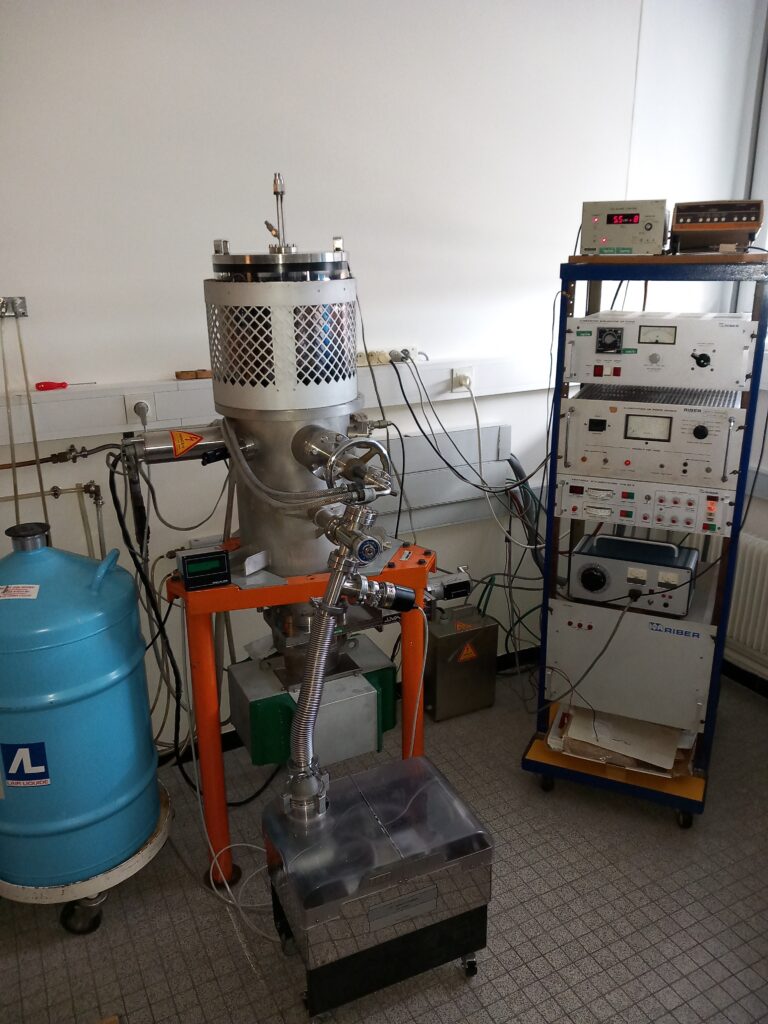

The Ultrafast Optics and Nanophotonics Department (DON) of the IPCMS
has an evaporation chamber equipped with an electron gun.
The most commonly deposed material with this device are Al, Ni, Ag, Co, Cr,
Cu, Pt, Au, and SiO2 as isolating materials.
This electron gun is equipped with three crucibles cooled down with water.
The three crucible allows the evaporation of 3 different materials without
breaking the vacuum.
The growth rate and the layer thickness are controlled by a quartz
microbalance.
The base pressure of the chamber is close to 10-7 mbar without wall
cooling or 10-8 mbar when the wall is cooled down. Such a vacuum is obtained
with an ionic pump assisted at the beginning by a scroll pump coupled with a turbomolecular
pump.
Contact :
Engineer

EVAPORATION (JOULE EFFECT)
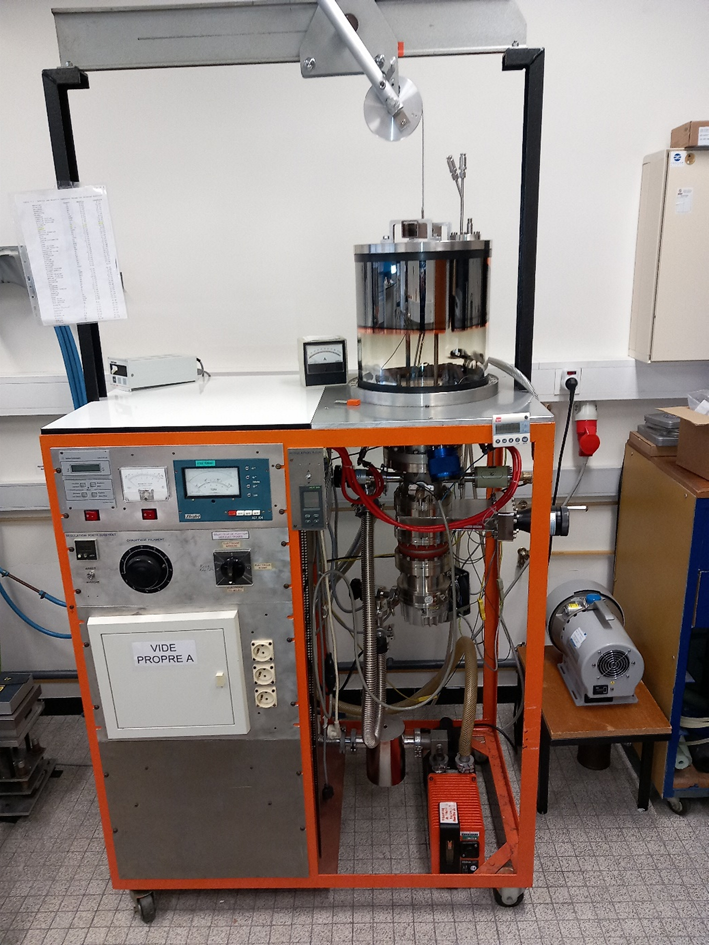

The Ultrafast Optics and Nanophotonics Department (DON) has a second evaporation chamber but this one is using joule effect
The most commonly deposed material with this device are Cu, Cr, Al and Au. This chamber is equiped with three crucibles done in refractory material. (Mo,W,Ta,…). The crucible can be replaced by coils or basket depending on the material which has to be evaporated.
The base pressure of the chamber is close to 10-6 mbar. Such a pressure is obtained with a primary rotary vane pump combined with a turbomolecular pump.
The growth rate and the layer thickness are controlled by a quartz microbalance.
Contact :
Engineer

SPUTTERING
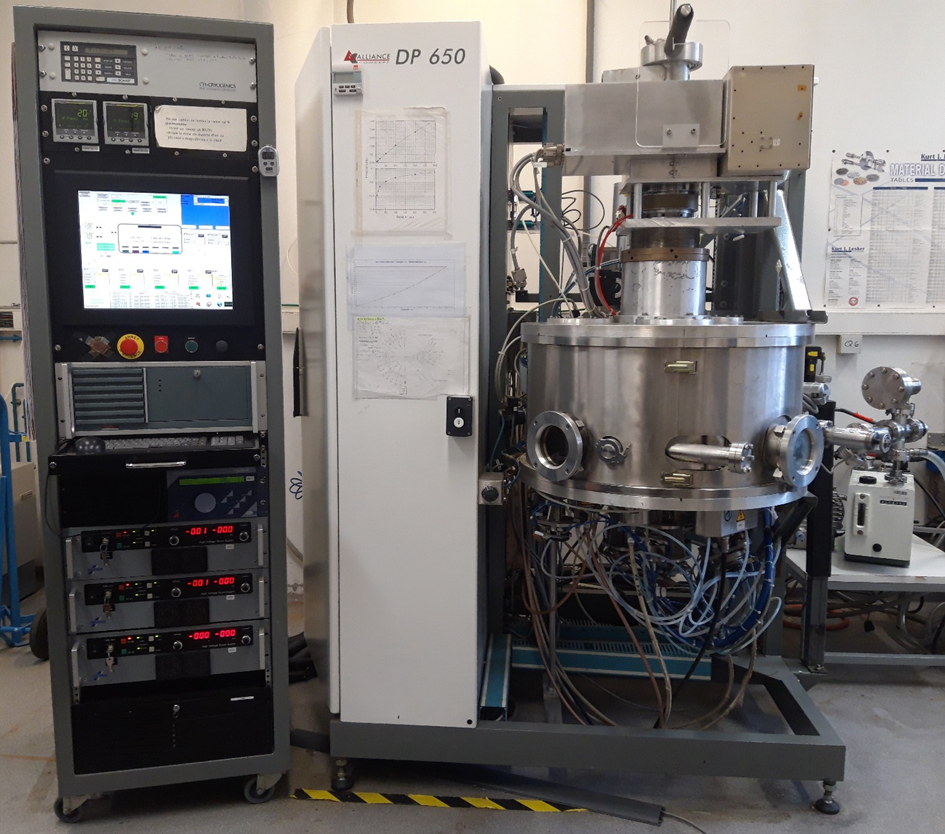

The IPCMS has within the Department of Magnetism and NanoStructured Objects (DMONS), a magnetron sputtering chamber in order to develop multi-layered samples: metals, oxides, nitrides… The chamber is equipped with 6 magnetrons with 4 power supplies (3DC and 1 RF), 9 sample holders on a cold station that can be regulated from -180°C to 100°C and 2 sample holders on a hot station that can go from 100°C to 800 °C. The base vacuum is of 5*10-7 mbar and the process pressure ranges from 10-3 to 5*10-2 mbar.
More informations about the equipment are available here
Contacts :
Engineer





