Benjamin BACQ-LABREUIL (IPCMS – DMONS)
Seminar DMONS – DCMI – Axis 5 presented by : Abhishake MONDAL
Abhishake MONDAL (Solid State and Structural Chemistry Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore)
Abstract :
The pursuit of smart multifunctional materials with stimuli-responsive magnetic and optical response has drawn escalating interest in both fundamental science and potential applications to switches, sensors, and intelligent devices.1 One of the appealing feature of such materials is the tunability of their physical property via chemistry, where the linking structure and physical properties can be modulated in practically infinite ways, which gives them an edge over the solid-state magnetic materials (Figure 1, a).2 The field of molecular bistable systems is rapidly budding towards utilizing these molecule-based magnetic materials in physics-driven and nanotechnology-driven fields (Figure 1, b).
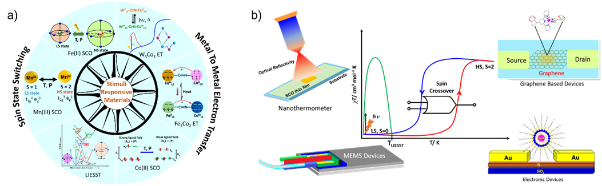
Figure 1: a) Stimuli-responsive molecular bistable systems and b) Application areas where these systems are actively studied for developing devices
Here, I will briefly cover the exciting field of Molecular Magnetism and will specifically focus on three most important aspects of Molecular Magnetism being pursued in my laboratory i) Spin Crossover (SCO) materials3 ii) Metal-to-Metal Electron Transfer Systems (MMET)4 and iii) Single Molecule Magnets (SMM).5 Lastly, I shall discuss the application of these bistable systems in developing ring-resonator devices for Photonics Application, molecular break junctions and microelectromechanical systems.
Acknowledgments: I thank the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, India, and the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India, IISc-Start-up Research Grant, the Department of Science and Technology, Mission on Nano Science and Technology (Nano Mission), Scheme for Transformational and Advanced Research in Sciences (STARS, MHRD), Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for the research fundings.
References:
1. Kamilya, S.; Dey, B.; Kaushik, K.; Shukla, S.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 4889, Kaushik, K.; Mehta, S.; Das, M.; Ghosh, S.; Kamilya, S.; Mondal, A., Chem. Commun., 2023, 59, 13107, Coronado, E., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 87. 2. Minguez Espallargas, G.; Coronado, E., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 533. 3. Ghosh, S.; Kamilya, S.; Pramanik, T.; Rouzieres, M.; Herchel, R.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A., Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 13009, Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.; Kamilya, S.; Mandal, S.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A., Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 17080, Bagchi, S.; Kamilya, S.; Mehta, S.; Mandal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Narayan, A.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, A., Dalton Trans., 2023, 52, 11335, Ghosh, S.; Bagchi, S.; Kamilya, S.; Mehta, S.; Sarkar, D.; Herchel R.; Mondal, A., Dalton Trans., 2022, 51, 7681. 4. Kamilya, S.; Ghosh, S.; Li, Y.; Dechambenoit, P.; Rouzières, M.; Lescouëzec, R.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A., Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 11879, Kamilya, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A., J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 4775. 5. Hossain, S. M.; Kamilya, S.; Ghosh, S.; Herchel, R.; Kiskin, M. A.; Mehta, S.; Mondal, A., Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 1656.
Quantum sciences and materials / QMat mini-symposium
Program :
09h00-09h30: Iann Gerber (LPCNO Toulouse)
Theoretical exploration of exciton-exciton interactions in 2H-transition metal dichalcogenide bilayers
09h30-10h00: Vincent Jacques (L2C, Montpellier)
Quantum sensing with spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride
10h00-10h30: Coffee break
10h30-11h00: Clément Faugeras (LNCMI, Grenoble)
Magneto-Raman scattering of a frustrated van der Waals magnet
11h00-11h30: Cyriaque Genet (ISIS, Strasbourg)
Taming a Maxwell’s demon for experimental stochastic resetting
The abstracts are available there.
Seminar DON / Axis 2 presented by Pr. Keiichi INOUE
Speaker : Pr. Keiichi INOUE (Functional Materials Group, The Inst. for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo)
Rhodopsins, or retinal proteins, are light-sensitive membrane proteins, with very important biological functions. In vertebrates, rhodopsins are the sensors for vision.
Pr. Inoue is a world-leading expert in the photochemical studies of microbial retinal proteins (https://www.icpworldcongress.com/keiichi-inoue). His research aims at a detailed molecular understanding of how the different biological functions of these rhodopsins are encoded in the structural and spectroscopic properties. The abstract can be found : here
Contact: Stefan Haacke (stefan.haacke@ipcms.unistra.fr)
Seminar Axis 1 “Quantum sciences and materials” presented by : Clément Pellet-Mary
Speaker: Clément Pellet-Mary, University of Basel, Switzerland
The abstract is available there.
Seminar Axis 1 “Quantum sciences and materials” presented by Cyrille SOLARO
Speaker: Cyrille Solaro, CESQ, Strasbourg
The abstract is available there.
Seminar DCMI and Axes 3 and 5 : presenetd by Raquel UTRERA MELERO
Abstract : Materials exhibiting luminescence stimuli-responsive properties, present potential application as detection systems. Among these materials, copper (I) iodide molecular clusters coordinated by phosphine ligands, exhibit thermochromic and mechanochromic luminescence properties. These compounds are characterized by a change of their emission wavelength in response to temperature or mechanical stress. The establishment of structure- properties relationships permit to study the mechanisms responsible for their properties. The main characterization techniques used are solid-state NMR, X-ray diffraction, Infrared and Raman spectroscopies. In addition to the thermo and mechanochromic properties, these compounds have the particularity of exhibiting aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties. The understanding of properties is crucial for applications. Therefore, DFT (Density Functional Theory) calculations are also carried out to rationalize the different results and in particular the optical properties. In the last years, copper has been proposed as a substituent in lead perovskite-based devices due to its non-toxic nature. We are currently investigating the use of copper perovskites for solar cells.
Seminar of Axis “Quantum sciences and materials” presented by Arthur Veyrat
Speaker : Arthur Veyrat, Laboratoire de Physique des Solides, Equipe MESO, Orsay
The abstract is available there.
Seminar DCMI-Axis 5 presented by Thomas Cottineau
Speaker : Thomas Cottineau (Equipe Photocatalyse & Photoconversion –
Institut de Chimie et Procédés pour l’Energie, l’Environnement et la Santé
(ICPEES UMR 7515 CNRS / Université de Strasbourg)
Seminar Axis 1 presented by Masha Kamenetska
Speaker: Masha Kamenetska, Univ. Boston


